Smarter AI Training with Few-Shot Natural Language Tasks
2 Oct 2025
AdaMix proves its edge in few-shot NLU, consistently outperforming full fine-tuning across GLUE benchmarks with BERT and RoBERTa.
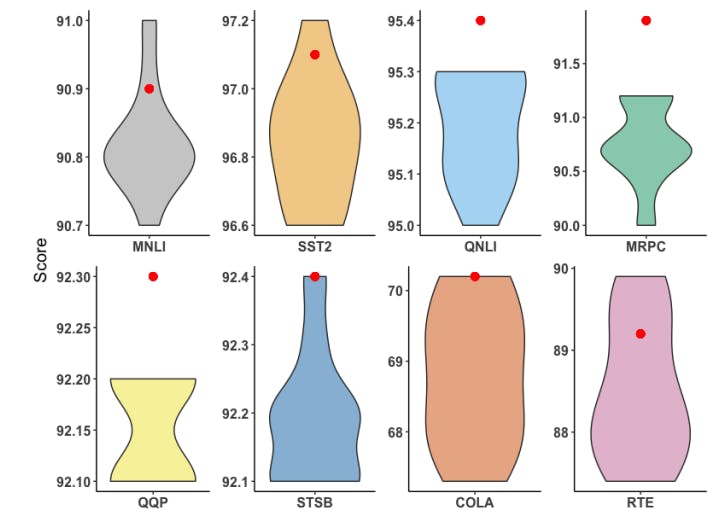
Beating Full Fine-Tuning with Just 0.2% of Parameters
2 Oct 2025
AdaMix improves fine-tuning of large language models by mixing adaptation modules—outperforming full tuning with just 0.2% parameters.
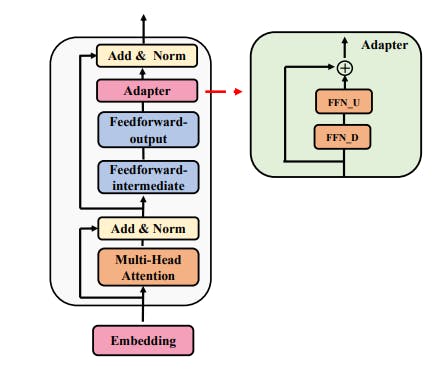
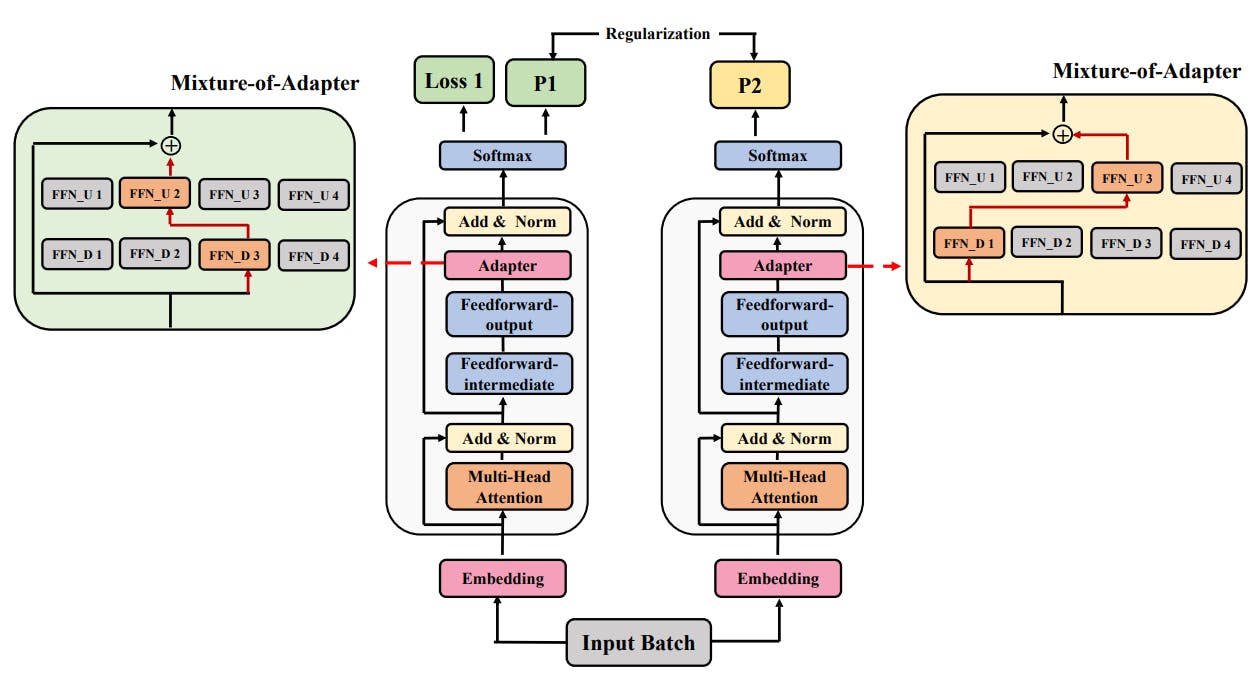
The Role of Consistency and Sharing in Efficient Fine-Tuning
1 Oct 2025
Ablation studies on AdaMix reveal why adaptation merging, consistency regularization, and module sharing drive superior fine-tuning performance.
Smarter Fine-Tuning for NLU and NLG Tasks
1 Oct 2025
AdaMix outperforms fine-tuning and top PEFT methods across NLU, NLG, and few-shot NLP tasks, proving both efficient and powerful.
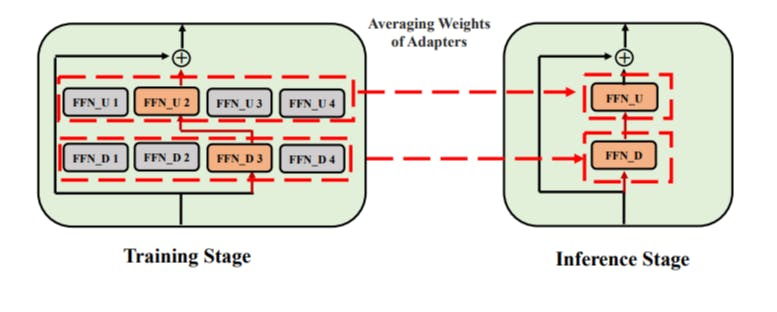
How Mixture-of-Adaptations Makes Language Model Fine-Tuning Cheaper and Smarter
1 Oct 2025
Discover how Mixture-of-Adaptations uses random routing and weight merging to fine-tune language models with less cost and better performance.
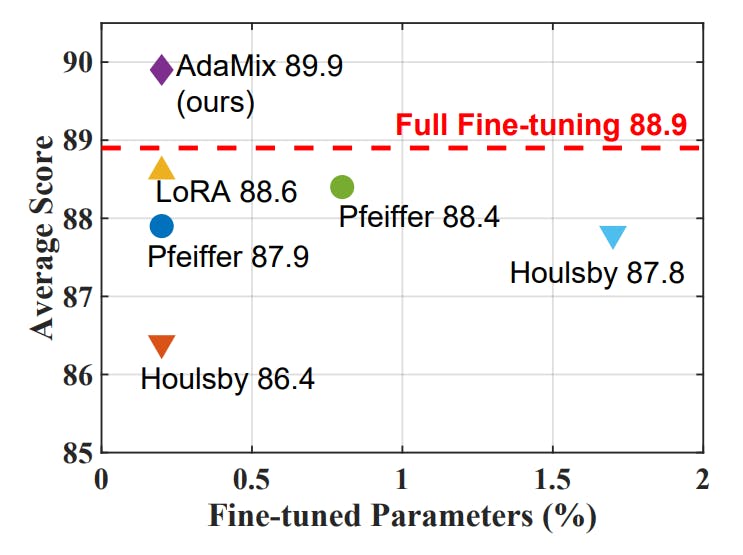
How to Improve AI Models While Training Only 0.1% of Parameters
1 Oct 2025
AdaMix fine-tunes large language models with just 0.1% of parameters, beating full fine-tuning in performance and efficiency.
Patient-Specific CNN-RNN for Lung-Sound Detection With 4× Smaller Memory
9 Sept 2025
Log-quant cuts model memory 4× with minimal accuracy loss; compute fits mobile SoCs, enabling real-time, wearable lung-sound screening.

Dataset, Features, Model, and Quantization Strategy for Respiratory Sound Classification
9 Sept 2025
Mel-spectrograms feed a CNN-RNN; last layers retrain on tiny patient sets, then log-quant weights trim memory 4× for wearables.

Patient-Specific CNN-RNN for Wheeze and Crackle Detection with 4× Memory Savings
9 Sept 2025
Hybrid spectrogram CNN-RNN outperforms VGG/MobileNet and shows that transfer learning solves data scarcity in respiratory AI.
